Understanding qEEG Brain Mapping
Learn how brain mapping works and how it can help identify the root causes of attention and learning challenges
Your brain generates electrical activity through an electrochemical process. This activity is what allows you to learn, focus, communicate, manage emotions, and carry out everyday tasks.
Brain mapping—also known as quantitative electroencephalography or qEEG—is a method of recording and analyzing this electrical activity in the form of brainwaves. These brainwaves vary in frequency depending on your mental state. For example:
- Slower brainwaves (Delta, Theta, Alpha) occur during sleep, daydreaming, or under-aroused states.
- Faster brainwaves (Beta, Gamma) are active when you are alert, attentive, and learning.
When the brain produces too many slow waves or not enough fast waves, its ability to function at an optimal level for learning, focus, and behavior can be compromised.
What Is qEEG Brain Mapping?
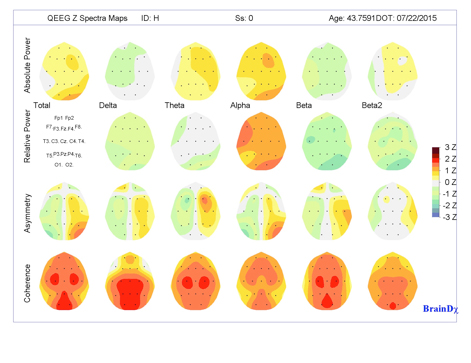
At the Center for Attention Deficit and Learning Disorders, we use qEEG to measure and map brainwave activity. These maps are displayed as color-coded images showing how different regions of the brain are functioning. The patterns can be compared to a large, age-matched database of healthy brainwave activity.
This comparison generates Z-scores, which are statistical measures that show how much a particular brain area deviates from the norm. These deviations can help identify areas of dysregulation or inefficiency.
How Are Brain Maps Used?
qEEG brain maps provide a foundation for developing individualized treatment plans. By identifying areas where brainwave activity is overactive or underactive, we can target those areas through non-invasive treatments such as neurofeedback.
This approach allows us to tailor ADD/ADHD treatments to each patient’s specific needs, based on how their brain is functioning—not just their symptoms.
What Is the Brain Mapping Process Like?
Recording a brain map is a safe, non-invasive procedure. Here’s what to expect:
- Sensor Placement: Nineteen sensors are placed on the scalp using the International 10-20 system—a standardized method for identifying precise locations on the brain.
- Recording Session: You’ll sit quietly for a short period while your brain’s electrical activity is recorded.
- Analysis: The data is reviewed by Dr. Silverman and our clinical team. We interpret the findings and create a personalized treatment plan based on the results.
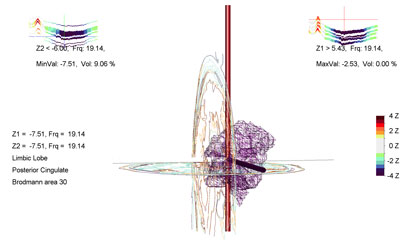
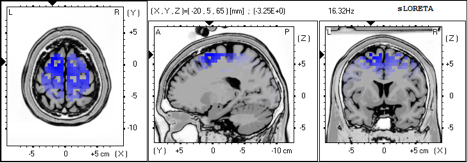
What Is LORETA Brain Mapping?
In some cases, we enhance standard qEEG analysis using LORETA (Low Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography). LORETA produces 3D images of brainwave activity, allowing us to visualize deeper structures within the brain—similar to an fMRI, but at a significantly lower cost.
LORETA can help detect functional abnormalities not visible through surface-level qEEG, making it especially helpful in complex cases.
Want to Learn More About Brainmapping and ADHD Treatment
If you’re curious about how qEEG brain mapping could help you or your child, we’re here to answer your questions.
Contact us to schedule a consultation or learn more about our brain-based approach to care.